![[What and How the Michelson Interferom-Demjanov.pdf]]
Ether wind papers: files.aethercosmology.com/s/EtherWindPapers
Preferred direction papers: files.aethercosmology.com/s/EtherWindPreferredDirection
GPS Variant speed of light papers: files.aethercosmology.com/s/GPSVariantSpeedofLight
Sagnac papers: files.aethercosmology.com/s/SagnacEffect
Who was behind the push of Einstein?
Relativity theory has been around for over a century now and to this day acolytes in support of the theory have completely surrendered their faculties to equations and concepts that they don’t fully understand or care to. The classical proofs of relativity are often cited to handwave dismiss any criticisms of the theory, despite supporters of the theory not even being able to describe what “spacetime” is exactly. This presentation attempts to make clarifications on what spacetime is and taking it a step further, I will make the case that spacetime has to be a physical entity if any curvature thereof was responsible for the physical effects that are attributed to it as proof of the theory.
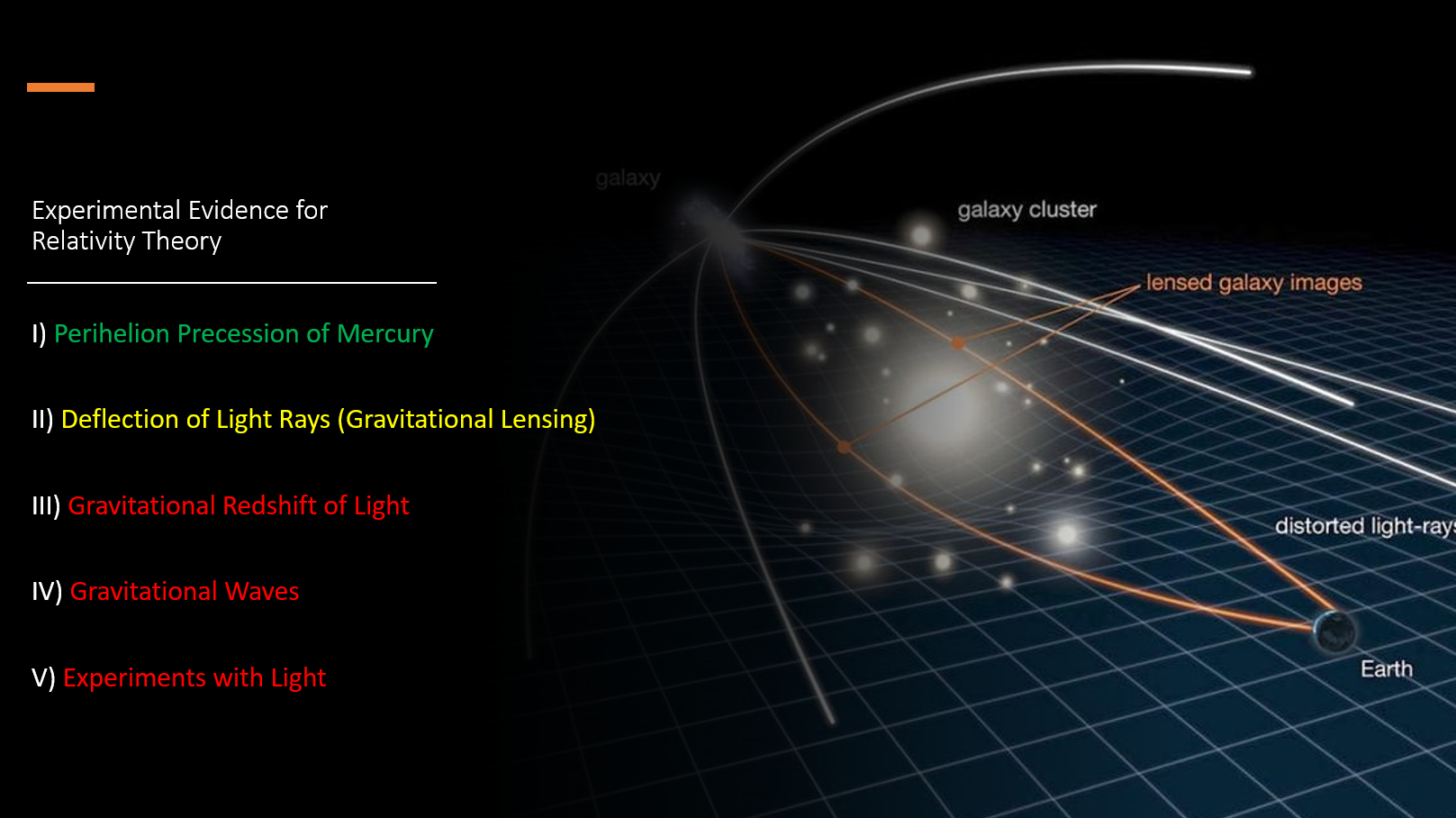
Classical Proofs of Relativity Theory: Perihelion precession of Mercury, deflection of light by the sun, gravitational redshift, misc. indirect confirmations of the theory (time dilation, equivalence principle, etc.).
If relativity theory were to supersede the Newtonian framework, it would need to prove the concept of “spacetime” is a physical entity that has a mechanical cause and effect relationship with how it interacts with physical objects and electromagnetic energy. Here we will examine the historical narrative and experiments that are put forward to support the physicality of spacetime.
It is my intention to use this presentation as a vehicle to provide clarification on relativity theory by demystifying and translating the equations, experimental proofs and mechanics used to as evidence for the theory.
•The geometry of spacetime is described using a mathematical construct called a metric tensor. How might one use regular metric tensor framework for practical purposes? Example: In engineering, you can use this framework to describe a Cartesian coordinate system (xyz axis) to define the dimensions of an I-beam. This can then be used to show how much stress will be exerted on any particular point within that coordinate system that describes the I-beam. You can even use it to show the stress relationship between two different points within the I-beam.
•Similarly, a spacetime metric tensor describes the geometry of spacetime by adding time (t) as a fourth axis to the xyz coordinate system (xyzt). In relativity theory, any axis of the coordinate system can be bent, warped, distorted, expanded or contracted.
•Objects in motion in relativity theory are described by the xyzt coordinate system as traveling on geodesic paths, i.e., straight lines. By adding the fourth dimension of time to the coordinate system, one can see outside of the xyz system to find that the straight lines are actually traveling along the curvature of spacetime. And remember, spacetime is the dimensions of the universe as described by the respective metric in use.
•Since xyzt coordinate system is relative, the maximum speed of light in a vacuum (c) is introduced as a constant that can be used to measure distance and time within the spacetime metric. In order for this system to describe reality, the speed of light must be shown to be the same in all reference frames. A quick note on reference frames: a reference frame is a way of describing relative motion between observers.
•It has been experimentally shown that c has variance to it. However, to mathematically demonstrate the presupposed axiom of c, which relativity theory is entirely built upon, equations known as Lorentz transformations are used to express how the coordinate system is being stretched or contracted in such a way as to explain the results of optical experiments using interferometry such as MMX, Sagnac, et el., which we will get into later in the presentation.

The perihelion precession of Mercury is the gradual shift in the position of Mercury's closest approach to the sun (perihelion) over time. In 1846, Urbain Le Verrier, observed and recorded a perihelion precession of Mercury as it orbits the sun. He calculated a perihelion precession to be 5600 arcseconds per century. Many years later, Newtonian mechanics and relativity theory faced off to account for the perihelion precession. Here are the results:
•Actual observed value: 5600 arcseconds per century
•Newtonian gravity post-diction: 5557 arcseconds per century
•Relativity theory post-diction: 5600 arcseconds per century
Newton’s mechanics were off by 43 arcseconds per century, while relativity theory, using a modified Schwarzschild’s metric, Einstein was able to match the observed 5600 arcseconds per century.
Getting people to accept this calculation as proof of GR was crucial. It redefines gravity as spacetime curvature and gives the appearance of giving physical solutions using mathematical concepts.
For clarification: This is NOT a prediction of GR, this is a postdiction.
A spectrograph is a scientific instrument used to analyze the spectral shift in light emitted by a source, such as a star, by separating it into its individual colors or wavelengths. This is done by directing the light through a diffraction grating or a prism, which splits the light into its component colors or refracts the light at different angles based on its wavelength. In the past, photographic plates were commonly used to record the resulting spectrum. By analyzing the spectrum shift, you can determine the energy and frequency of the wavelength of light, which can provide information about what happened to the light during its journey. For example, light traveling through a gravitational field is expected to lose energy, causing a frequency shift and wavelength decrease, resulting in a red spectrum shift known as "gravitational redshift." This is different from a velocity shift, or Doppler shift, which can be determined by observing whether the light is blueshifted or redshifted depending on whether the source is moving towards or away from the observer.
General relativity attempts to distinguishes between redshift due to velocity shift, which is caused by relative motion, and redshift caused by relativistic conditions such as traveling through a gravitational field along the curvature of spacetime. In the case of gravitational redshift, light traveling through a gravitational field loses energy, which results in a decrease in frequency and an increase in wavelength, resulting in a redshift of the light. The spectral shift phenomenon, after presupposed corrections are made and correct transformations applied; relativistic results can be extrapolated from experiment and then attributed to the theory.

Paul Gerber was a physicist who attempted to modify Newtonian mechanics by proposing a medium for gravitational waves to propagate through. He derived his equations from classical wave theory and implemented a velocity-dependent potential correction to explain the perihelion precession of Mercury in 1898. His theory was simple and effective, correctly accounting for the observed perihelion precession of Mercury, and even imposed a speed limit on gravitational waves by adding a medium for them to propagate through. Despite the success of his equations in matching observations, the notion of a medium for gravitational waves could not be derived from Newton's theories and was therefore rejected. Gerber was unable to explain the physical mechanism by which the gravitational influence propagated through the proposed medium, which ultimately led to the rejection of his theory, despite the mathematical accuracy of his equations..
Gerber’s equation: ψ = 24π³ a²/(τ²c²(1-ϵ²))
Since Gerber’s time, there have been many successful attempts to use Newtonian mechanics to explain the precession just as accurately as Einstein’s equations. However due to some mysterious non-complete clause that seems to be enacted, no other theoretical explanation is seriously considered even though they’re just as mathematically valid and no distinction can be made between predictions made by relativistic effects and classical wave theory.
•Ψ (psi): This is the gravitational potential of the Sun, caused by the mass of the Sun attracting the mass of Mercury.
•a: This is the semi-major axis of Mercury's orbit around the Sun.
•Τ (tau): This is the time it takes for the gravitational influence of the Sun to propagate through a medium from the Sun to Mercury.
•c: This is the speed of light.
•ϵ (epsilon): This is the eccentricity of Mercury's orbit.

Arthur Eddington
•"We know that momentum is carried along on the path of a beam of light. Gravity in acting creates momentum in a direction different to that of the path of the ray and so causes it to bend. For the half-effect we have to assume that gravity obeys Newton's law; for the full effect which has been obtained, we must assume that gravity obeys the new laws proposed by Einstein. This is one of the most crucial tests between Newton's law and the proposed new law. Einstein's law had already indicated a perturbation causing the orbit of Mercury to resolve. That confirms it for relatively small velocities. Going to the limit, where the speed is that of light, the perturbation is increased in such a way as to double the curvature of the path, and this now confirmed.
•This effect may be taken as proving Einstein's law rather than his theory. It is not affected by the failure to detect the displacement of Fraunhofer lines on the Sun. If the latter failure is confirmed it will not affect Einstein's law of gravitation, but it will affect the views on which the law was arrived at. The law is right, though the fundamental ideas underlying it may yet be questioned."
•"One further point must be touched upon. Are we to attribute the displacement to the gravitational field and not to refracting matter around the Sun? The refractive index required to produce the results at a distance of 15' from the Sun would be that given by gases at a pressure of 1/60 to 1/200 of an atmosphere. This is of too great a density considering the depth through which the light would have to pass."




Ken Wheeler Demonstrating Electromagnetic Retardation
[https://youtu.be/47T1_5P8jtg](https://youtu.be/47T1_5P8jtg)


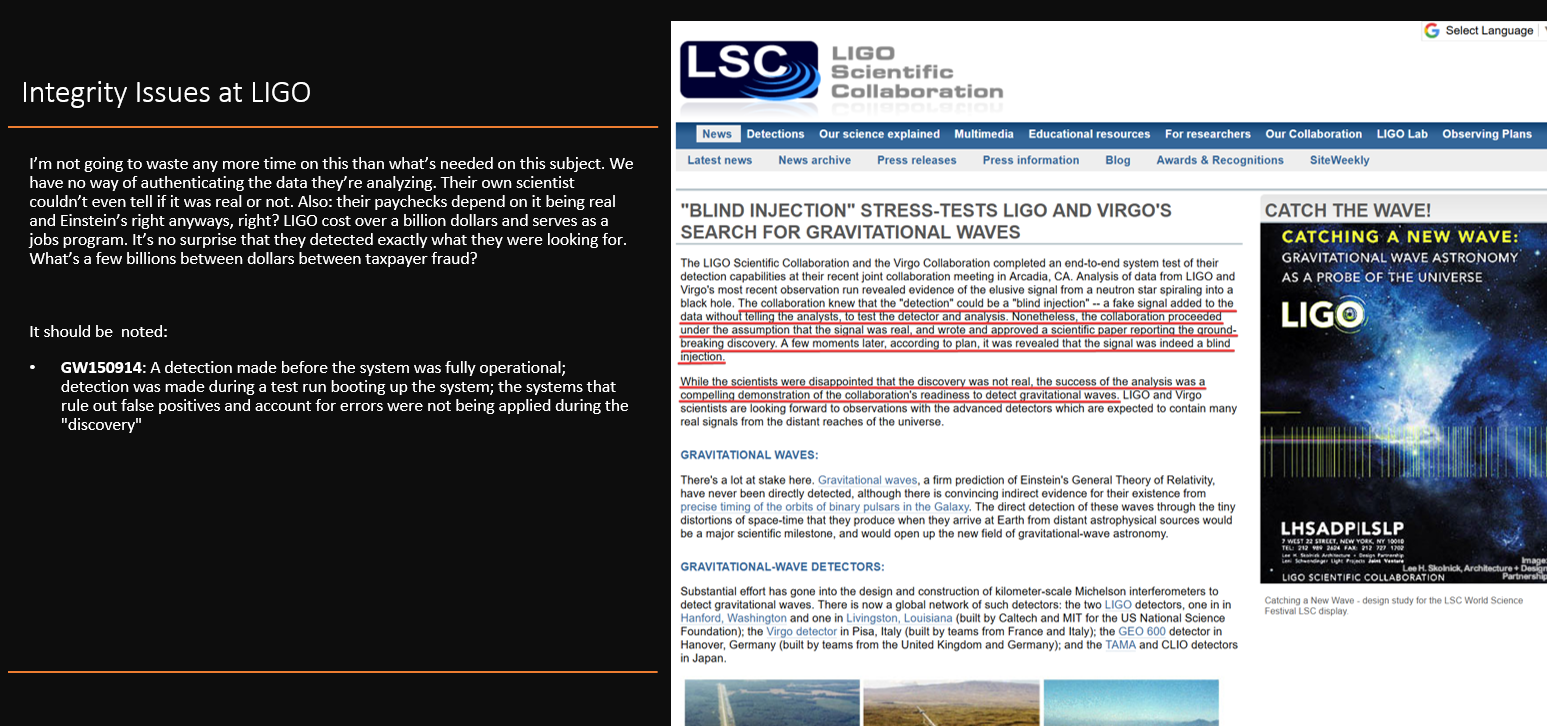
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime caused by the collision of massive objects (in this case: black holes). They were predicted by Einstein's theory of General Relativity in 1915 and were finally detected in 2015 by LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory). The detection provided direct evidence of the existence of gravitational waves and confirmed a key aspect of Einstein's theory.
LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) is designed to detect gravitational waves. It consists of two detectors, one in Hanford, Washington and the other in Livingston, Louisiana, which use laser interferometry to measure extremely small distortions in spacetime caused by passing gravitational waves. The lasers shoot beams of light down long tubes, and any warping of spacetime caused by a passing gravitational wave will change the relative distance between the beams, causing a detectable change in the interference pattern. By comparing the data from both detectors, LIGO can identify and measure the signature of gravitational waves passing through the Earth.
•





In conclusion the historical and classical experimental evidence put forward as proof of the theory of relativity does not support it and has entirely collapsed in on itself (at free fall free fall speeds) and has been revealed to be mathematical prank played on us all. In my opinion, there was a deliberate effort to promote the theory of relativity and make it widely accepted. Someone or a group of individuals realized that they could utilize the framework of spacetime curvature interpretation to manipulate the concept of time and natural electromagnetic phenomena. This was done by using spacetime metaphors supported by mathematics.
The terms "spacetime" or "spacetime curvature" are misleading and imaginary. There is no experimental proof that the theory of relativity is anything beyond a mathematical framework. Spacetime possesses no physical attributes and cannot distort time or alter the path of mass or massless objects moving along a nonexistent curvature.
Some individuals may think that the theory of relativity has been verified because its predictions have been validated on several occasions. However, other concepts like Lorentz ether theories also produce comparable outcomes. The issue with the theory of relativity is that it employs mathematics to predict successfully, but the way it describes time and space is illogical and even goes against established knowledge. The underlying problem arises from the switch from Lorentz's concept of absolute time and variable light speed to Einstein's idea of relative time and constant light speed.
The Sagnac effect demonstrates that the speed of light can vary based on the observer's position, which can make time appear to pass differently. The major difference between the two systems is that Lorentz's system implies that stars, planets, galaxies, and other celestial objects are closer to us and exist in a denser medium. In contrast, the theory of relativity is essentially the inverse of the aether theory of a closer and denser medium. This allows for a broader range of interpretations concerning distances, sizes, and the nature of the so-called vacuum of space. The reason why mainstream science can state with a straight face that a photon that has traveled for 13.7 billion years to reach our eyes has covered 80,600,000,000,000,000,000,000 miles is due to the inversion of the constant speed of light and relative time.
Experiments should guide the progression and validation of theories rather than theories influencing the results of experiments so that the data can selectively be used to confirm the theory.
# On Atomic Clock Synchronization, Time Dilation, and Michelson-Morley
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPHqe6p9Qfo&ab_channel=SpaceAudits](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPHqe6p9Qfo&ab_channel=SpaceAudits)