- Credits
- Section Writer: [[Dr. Om J Lakhani]]
- Section Editor: [[Dr. Om J Lakhani]]
- Q. What is the definition of Fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes (FCPD)?
- Diabetes associated with non-alcoholic calcific pancreatitis seen in developing countries
- Q. What is the prediabetic form of FCPD?
- It is called tropical calcific pancreatitis (TCP)
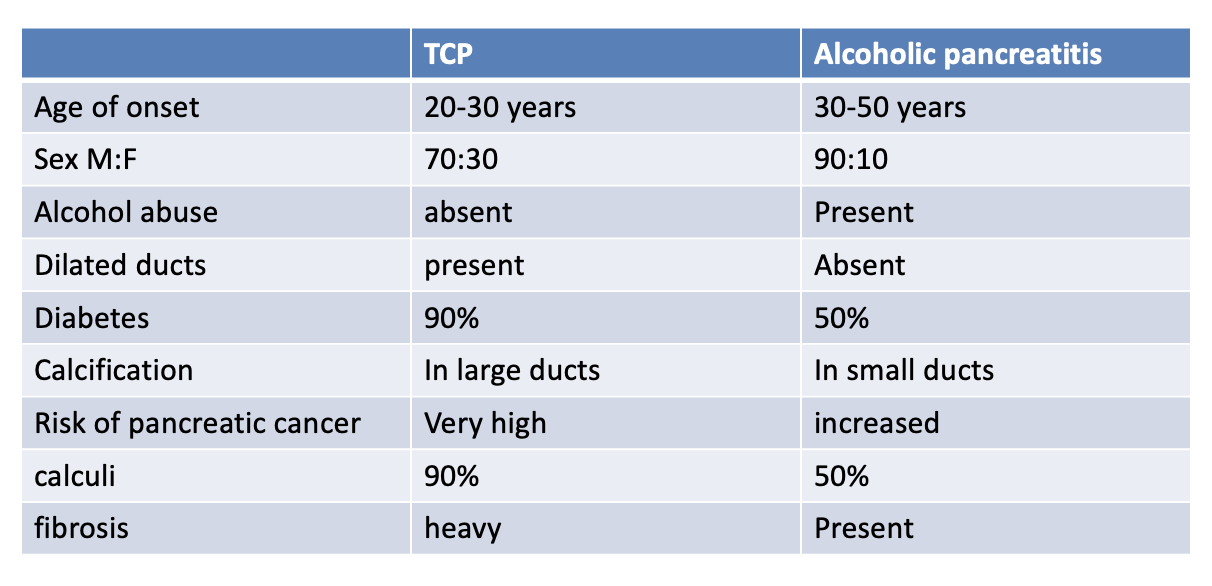
- Q. Give the difference between TCP and Alcoholic pancreatitis?
- 
- Q. Who is the father of FCPD?
- Geeverghese
- Q. Which are the two types of malnutrition-related DM (MRDM)?
- Fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes
- Protein deficient diabetes mellitus
- Q. What is the typical triad of FCPD?
- Abdominal pain- the first symptom- in childhood
- Pancreatic calculi- In adolescent
- Diabetes – in adulthood
- Q. Where is the calcification seen in Plain Xray in FCPD?
- Close to L1/L2 vertebra
- Q. Ketosis is present in FCPD. True or false?
- False
- Patients with FCPD do not develop ketosis
- Q. Intake of which food substance is implicated in causing FCPD?
- Cassava
- Q. Which cancer risk is increased in FCPD ?
- Pancreatic cancer
- Q. There are no microvascular complications in FCPD, True or false?
- False
- It was believed earlier but no so anymore
- Microvascular complications are very much present in patients with FCPD
- Q. What are the diagnostic criteria for FCPD?
- As given by Mohan et al
- Essential criteria
- Diabetes present
- Patient from a tropical country
- Absence of any other cause of pancreatitis
- Any 3 of the following
- Abnormal morphology of pancreas on imaging
- Abnormal pancreatic function test
- Abdominal pain –recurrent since childhood
- Steatorrhea
- Q. Which is the tumor marker for pancreatic cancer?
- CA 19-9
- Q. What is the classical clinical description of a patient with FCPD?
- Cyanotic hue
- emaciated
- Parotidomegaly
- Abdominal distention
- Q. Why is there no ketosis in FCPD?
- Some of the theories for absence of ketosis in FCPD are as follows
- No non-esterified fatty acid hence less substrate for ketosis
- Also there is reduced glucagon along with insulin
- High glucagon and reduced insulin is required for ketosis to develop
- The fat present is resistant to lipolysis
- There is some eesidual beta-cell function
- Carnitine deficiency – prevents Fatty acid entering the mitochondria for beta-oxidation
- Q. Is the calcification present in the parenchyma or in the duct ?
- FCPD- in the duct
- Alcoholic pancreatitis – in the parenchyma
- Q. What is the composition of the calculi ?
- It is composed of calcium carbonate
- Q. Can ERCP and EUS be used to define pancreatic morphology in FCPD ?
- Yes
- Q. Which is the invasive test for detecting pancreatic function ?
- Injection of secretin and Pancreozymin
- Collection of pancreatic juice
- Juice contains less of lipase, bicarbonate and trypsin compared to normal
- Q. Which are non-invasive (tubeless tests for pancreatic function) ?
- BT-PABA (Bentriomide para aminobenzyoic acid) - Urine / plasma
- Fecal elastase
- Fecal chymotrypsin
- Q. Which is the gold standard Tubeless test ?
- Fecal elastase
- Q. How Is endocrine pancreatic function tested for in FCPD ?
- Using C-peptide
- The value is intermediate between type 1 and type 2 – suggestive of residual pancreatic function
- Q. What is done for abdominal pain in FCPD ?
- It occurs earlier
- Non-opiod / opiod analgesisc are used
- It resolves once the endocrine dysfunction occurs
- Pancreatic enzyme supplementation does not reduce the pain
- Q. What is done for non resolving pain ?
- ESWL + ERCP
- Celiac plexus block
- Surgery drainage procedures – ductal decompression or pancreaticojejunostomy
- Surgery ablative procedures – partial or subtotal pancreatectomy
- Q. What is done for the management of steatorrhea?
- Pancreatic enzyme supplementation
- Reduce diet fat
- Give vitamins
- Q. What is the dose of pancreatic enzyme supplementation in these patients?
- Typical brand name is "Creon" 10,000 units before each meal
#Clinicalpearl
- In clinical practice is is observed that giving pancreatic enzyme supplement also has some beneficial effect on glycemic control. Some experts have suggested a link between the exocrine and endocrine dysfunctions.
- Q. What is the best treatment of diabetes in these patients?
- 85% require insulin
- Some may do well with OAD because of residual pancreatic function
- However, incretin-based therapies are best avoided
- They often have brittle diabetes and prone to hypoglycemia
- Q. What is done for nutrition ?
- Diet rich in proteins and carbs are given to combat the malnutrition
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Avoid fat – to reduce steatorrhea
- Q. Enlist the pathogenic factors for FCPD?
- Malnutrition
- Protein deficiency
- Cassava toxicity
- Oxidative stress
- Genetic and familial causes
- Q. Which are the cyanogenic glycosides present in cassava?
- Linamarin
- Lotaustralin
- Q. What are the investigations done to diagnose FCPD ?
- Tests to detect pancreatic function-
- Test to detect pancreatic morphology - Xray, USG , EUS, ERCP, etc
- Q. Which are the tests to detect pancreatic function?
- Fecal elastase
- Fecal chymotrypsin
- Fecal immunoreactive lipase
- Q. Enlist the complications associated with FCPD?
- Pancreatic cancer- 100 times increased risk
- Retinopathy and other microvascular complications
- Pancreatic osteodystrophy – malnutrition + malabsorption + diabetes = severe osteoporosis
- Pancreatic exocrine deficiency
- Q. Enlist the treatment options for FCPD?
- Diabetes management
- Exocrine pancreatic enzyme replacement
- Fat-soluble vitamin replacement- intramuscularly
- Pain management
- Endotherapy- ESWL + ERCP
- Early cancer detection
- Surgical therapy- mainly for the pain
- #Updates
- Date: Monday, 19 April 2021
- Source: Review article: Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of diabetes in fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes ^[Dasgupta R, Naik D, Thomas N. Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of diabetes in fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes. J Diabetes. 2015 Nov;7(6):754-61. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12280. Epub 2015 May 6. PMID: 25707547.]
- Q. Is malnutrition a cause or effect of FCPD?
- Recent studies suggest malnutrition is an effect rather than the cause of FCPD
- Q. Enlist the various theories for FCPD over time?
- Cassava theory – Geerverghese and McMillin
- Increase oxidative stress theory
- Genetic theory – recent theory
- Q. Which genetic mutation has been associated with FCPD ?
- SPINK1
- PRSS1 and PRSS2
- Chymotrypsinogen C
- Q. Diabetes onset is at what age ?
- Generally age 20-30 years
- About 1-2 decade after first episode of abdominal pain
- Q. Is insulin secretory defect established in FCPD?
- Yes
- Q. Is the exocrine and endocrine deficiency linked?
- It seems from some of the studies done by Yajnik et al
- Q. What is the newer paradigm in the etiology of diabetes in FCPD?
- New interest in FCPD is directed to insulin resistance as a cause of diabetes in FCPD
- Q. What is the link between insulin resistance and chronic pancreatitis?
- Some studies have shown that patient with pancreatic diabetes have hepatic insulin resistance due to internalization of hepatic insulin receptors and GLUT2
- The role of the pancreatic polypeptide has also been proposed
- Q. What is the role of a pancreatic polypeptide?
- Studies have shown that pancreatic polypeptide regulates the expression of the IR gene in the liver
- Thus impairment of PP will impair glucose homeostasis via IR gene expression in liver
- Q. Do patients with FCPD have insulin resistance similar to Type 2 diabetes patients?
- Yes
- This is according to a study by Mohan et al
- So FCPD patients have insulin resistance similar to type 2 diabetics!
- Q. Is the BMI in these patients showing something else?
- Singla et al. showed that these patients have higher body fat percentage despite low BMI
- This could contribute to the insulin resistance
- Q. What is the vicious cycle of glucagon and insulin?
- As far as 35 years ago, it was proposed that diabetes is not just an insulin problem but also a problem with glucagon
- Insulin resistance increases insulin production and secretion → higher intra-islet insulin concentration → increase glucagon production → further increase insulin secretion → vicious circle
- Q. Is glucagon indeed depleted in patients with FCPD?
- This theory is questioned now
- Some studies by Mohan and Yajnik have shown that FCPD may have preserved glucagon response and selective damage to beta cells
- Q. What is the role of incretin hormones in the pathogenesis of diabetes in chronic pancreatitis
- Knop et al. suggested that CP without diabetes had an intact incretin response compared to CP with diabetes
- This may be the missing link in FCPD
- Also, he showed that pancreatic enzyme replacement might augment incretin response- a theory that could have an impact on the management of FCPD
- Q. What is the role of body composition causing diabetes in FCPD?
- There is a theory that the lack of fat tissue may be to lipodystrophy like effect, which can lead to insulin resistance in FCPD patients
- Deficiency fat stores increase hepatic triglyceride stores → increase circulating fatty acids → improve insulin resistance
#Real-life-cases
Date - Monday, 19 April 2021
- A 30 year old male presented with history of unintentional weight loss
- His weight reduced from 100 kg to 70 kg over a period of 3 months
- During this process the patient was found to have hyperglycemia
- The patient was started on insulin, some weight was regained but over a few weeks he started developing hypoglycemia
- Insulin was stopped and the patient was started on Oral antidiabetics by his physician
- At age of 25, he had recurrent episodes of abdominal pain which were never investigated
- When he came to us he had an HbA1c of 10%
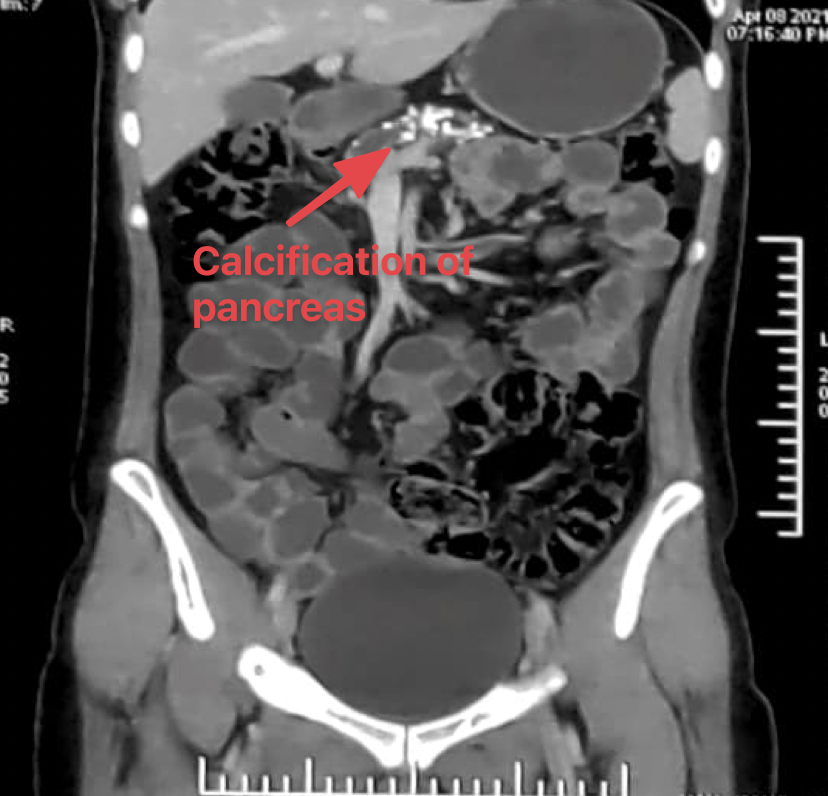
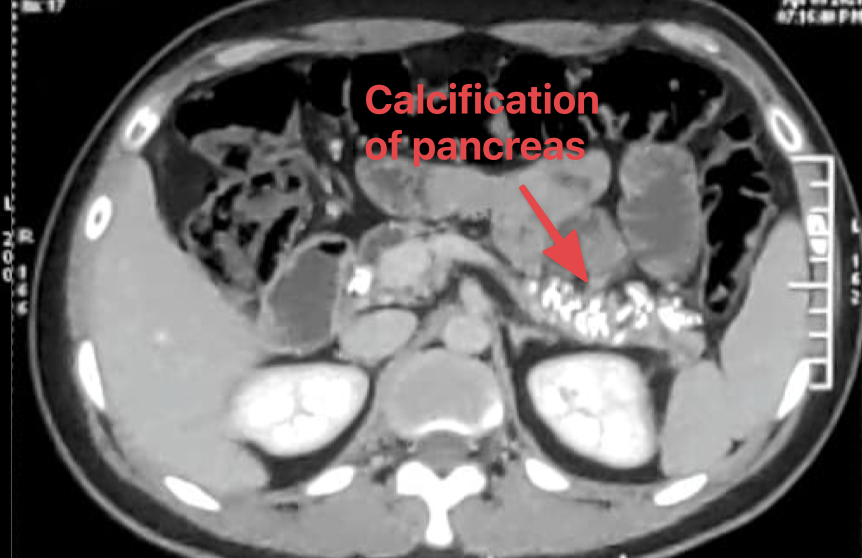
- Looking at the unusual history, we decided to perform a CT scan of the abdomen
- True to what we suspected, we found the pancreas studded with calcification
- 
- 
- There was no evidence of malignancy - however the risk and screening for the same has been explained to the patient
- The patient was restarted on insulin and pancreatic enzyme supplementation along with nutritional replenishment
- Currently he has regained some weight and maintain good glycemic control
Things to learn from the case:
- Sometimes a diagnosis of FCPD can be made retrospectively !
- In patients with acute symptomatic hyperglycemia- if the [[Glucose Toxicity (Glucotoxicity)]] breaks- the patient can start developing hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is higher in patients with FCPD
- Abdominal pain can disappear over a period of time. At later age the patient may present with just exocrine and endocrine insufficiency
- This patient is from Rajasthan. FCPD is not restricted to some regions of the country and can be considered a pan-Indian issue
#Updates ; Date: Friday, 9 July 2021
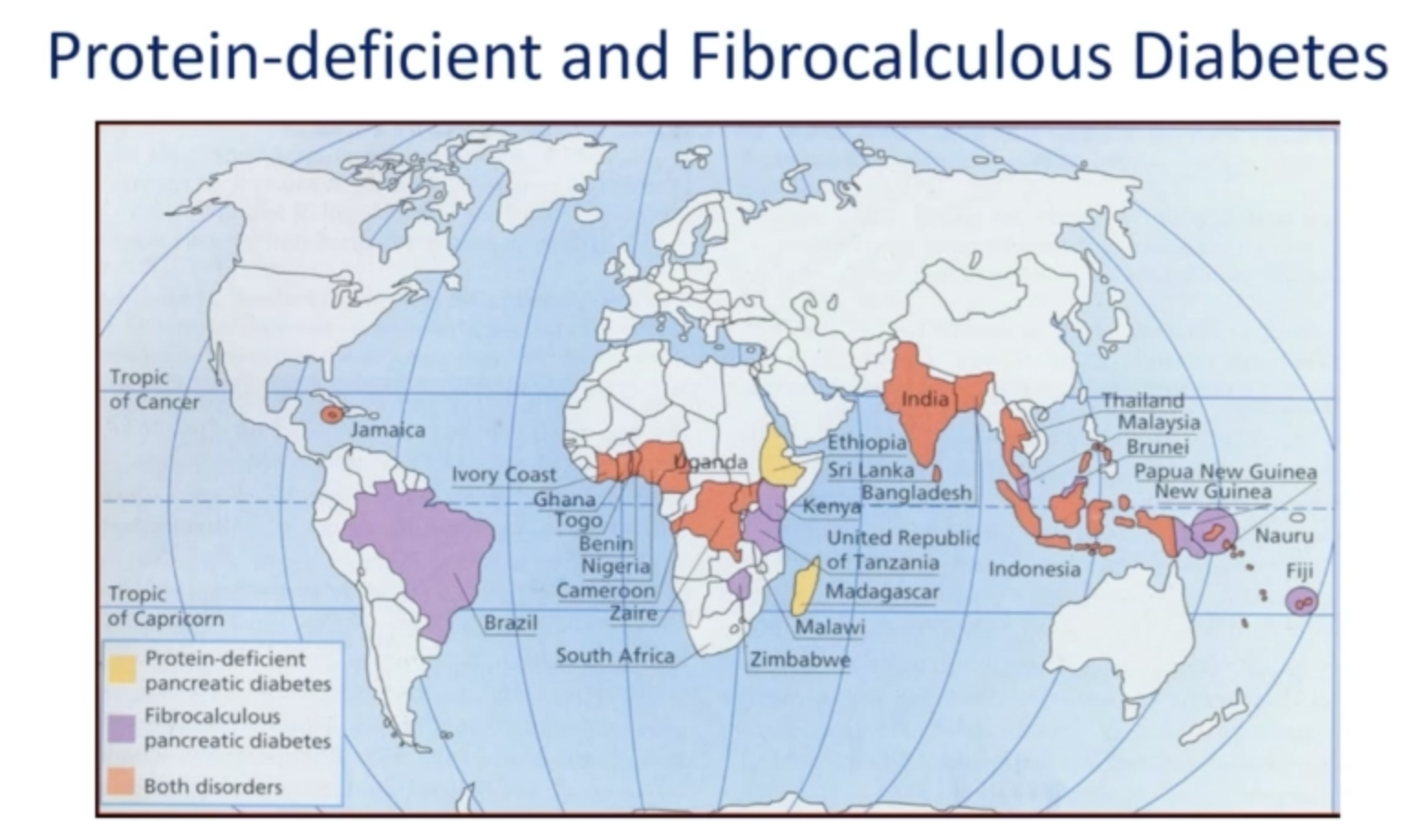
- Q. Can you give a map of regions in the world in which [[Fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes]] is seen ?
- 
----
Please consider donating to *"Notes in Endocrinology"* to keep us going. Please visit our [[DONATION]] page to know more