### Date : 2024-07-28 17:47
### Topic : Budget Constraints of Consumers #macroeconomics #economics #microeconomics
----
### Budget Constraints
**Definition:**
A budget constraint represents the limitations on the consumption choices of an individual or a household based on their income and the prices of goods and services. It defines the combinations of goods and services that can be purchased given a specific level of income.
#### Key Concepts
1. **Income:**
- The total amount of money available to a consumer for spending on goods and services. It can include wages, salaries, dividends, interest, and other sources of income.
2. **Prices of Goods and Services:**
- The cost per unit of goods and services that a consumer can buy. These prices determine how much of each good or service can be purchased with a given income.
3. **Utility Maximization:**
- Consumers aim to allocate their income in a way that maximizes their utility (satisfaction) within the limits set by their budget constraints.
#### Mathematical Representation
The budget constraint can be represented mathematically by the equation:

This equation states that the total spending on goods X and Y cannot exceed the consumer's income.
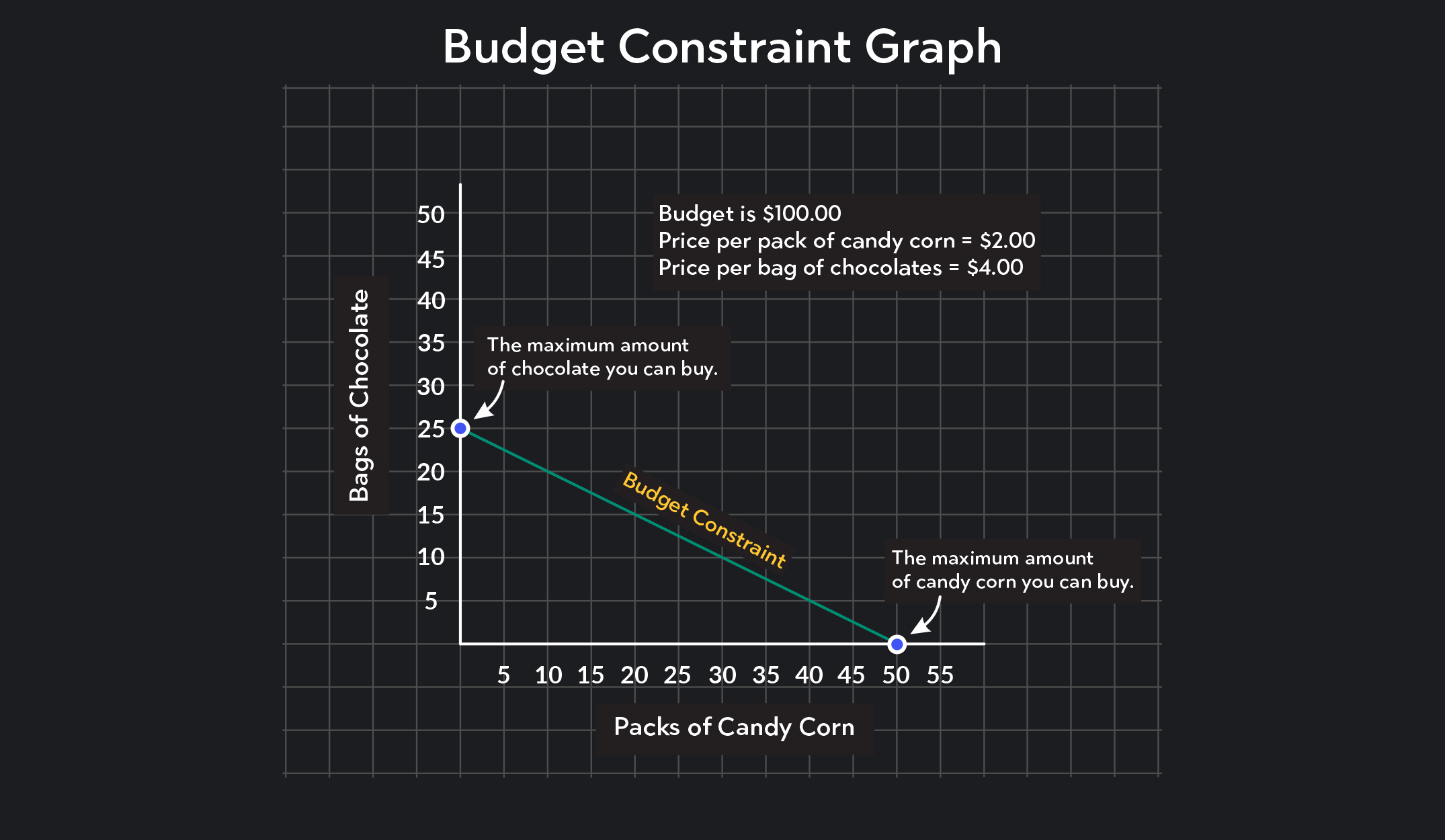
#### Graphical Representation
In a two-dimensional graph, a budget line can represent the budget constraint:
- The **slope** of the budget line is determined by the ratio of the prices of the two goods, \( -\frac{P_x}{P_y} \).
- The **intercepts** on the axes show the maximum quantities of each good that can be purchased if all income is spent on one good.
#### Shifts and Rotations
1. **Income Changes:**
- An increase in income shifts the budget line outward, allowing for the consumption of more goods.
- A decrease in income shifts the budget line inward, reducing the consumption possibilities.
2. **Price Changes:**
- A change in the price of one good will rotate the budget line around the intercept of the other good.
- For example, if the price of good X decreases, the budget line becomes flatter, indicating that more of good X can now be purchased for the same amount of good Y.
#### Applications
1. **Consumer Choice:**
- The concept of a budget constraint is fundamental in understanding consumer behavior. It explains how consumers make choices based on their preferences, prices, and income constraints.
2. **Demand Analysis:**
- By analyzing how changes in prices and income affect the consumption choices, economists can predict how demand for goods and services will change under different economic conditions.
3. **Policy Implications:**
- Understanding budget constraints can help in designing policies like tax changes, subsidies, and social welfare programs, as these can alter consumers' effective income and thus their consumption patterns.
### Conclusion
Budget constraints are a fundamental concept in economics, representing the limits on consumer spending based on income and prices. They are crucial for understanding consumer choices, market demand, and the overall functioning of the economy. By analyzing budget constraints, economists can gain insights into how changes in income and prices influence consumption decisions.
### Reference:
-
### Connected Documents:
- [[General Equilibrium Theory]]